InteractVLM: 3D Interaction Reasoning from 2D Foundational Models
 Teaser: Semantic Human Contact and Joint 3D Reconstruction
Teaser: Semantic Human Contact and Joint 3D Reconstruction
Abstract
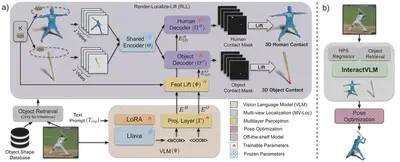
We introduce InteractVLM, a novel method to estimate 3D contact points on human bodies and objects from single in-the-wild images, enabling accurate human-object joint reconstruction in 3D. This is challenging due to occlusions, depth ambiguities, and widely varying object shapes. Existing methods rely on 3D contact annotations collected via expensive motion-capture systems or tedious manual labeling, limiting scalability and generalization. To overcome this, InteractVLM harnesses the visual knowledge of large Vision-Language Models (VLMs), fine-tuned with limited 3D contact data. We propose a Render-Localize-Lift module that:
- Render: Embeds 3D body and object surfaces into 2D space via multi-view rendering.
- Localize: Trains a multi-view localization model (MV-Loc) to infer precise 2D contact points.
- Lift: Projects the localized 2D contacts back to the 3D mesh.
Additionally, we define a new task—Semantic Human Contact—which conditions contact estimation on object semantics, going beyond binary labels to infer object-specific interaction regions. InteractVLM significantly outperforms prior art on contact estimation benchmarks and facilitates joint 3D reconstruction from a single image.
Teaser

Joint Human–Object Reconstruction
Accurate joint 3D reconstruction of human and object from a single image.
Method Overview
Comparison: InteractVLM vs. PHOSA
Joint Reconstruction Comparison

Input Image

PHOSA

InteractVLM
Semantic Human Contact Estimation
Contact Estimation Comparison

Input Image

DECO

InteractVLM
Object Affordance Prediction
Affordance Comparison

Input Image

PIAD

InteractVLM
Summary Video
Acknowledgments & Disclosure
We thank Alpár Cseke for assistance with joint reconstruction evaluation; Tsvetelina Alexiadis and Taylor Obersat for MTurk studies; Yao Feng, Peter Kulits, Markos Diomataris for feedback; and Benjamin Pellkofer for IT support. SKD is funded by IMPRS-IS; UvA work by ERC Starting Grant STRIPES (101165317). DT received Google research funding. MJB’s involvement was solely supported by the Max Planck Society.
Contact
For technical questions: sai.dwivedi@tue.mpg.de
For licensing: ps-licensing@tue.mpg.de
BibTeX
@inproceedings{dwivedi_interactvlm_2025,
title = {{InteractVLM}: {3D} Interaction Reasoning from {2D} Foundational Models},
author = {Dwivedi, Sai Kumar and Antić, Dimitrije and Tripathi, Shashank and Taheri, Omid and Schmid, Cordelia and Black, Michael J. and Tzionas, Dimitrios},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
month = {June},
year = {2025},
}